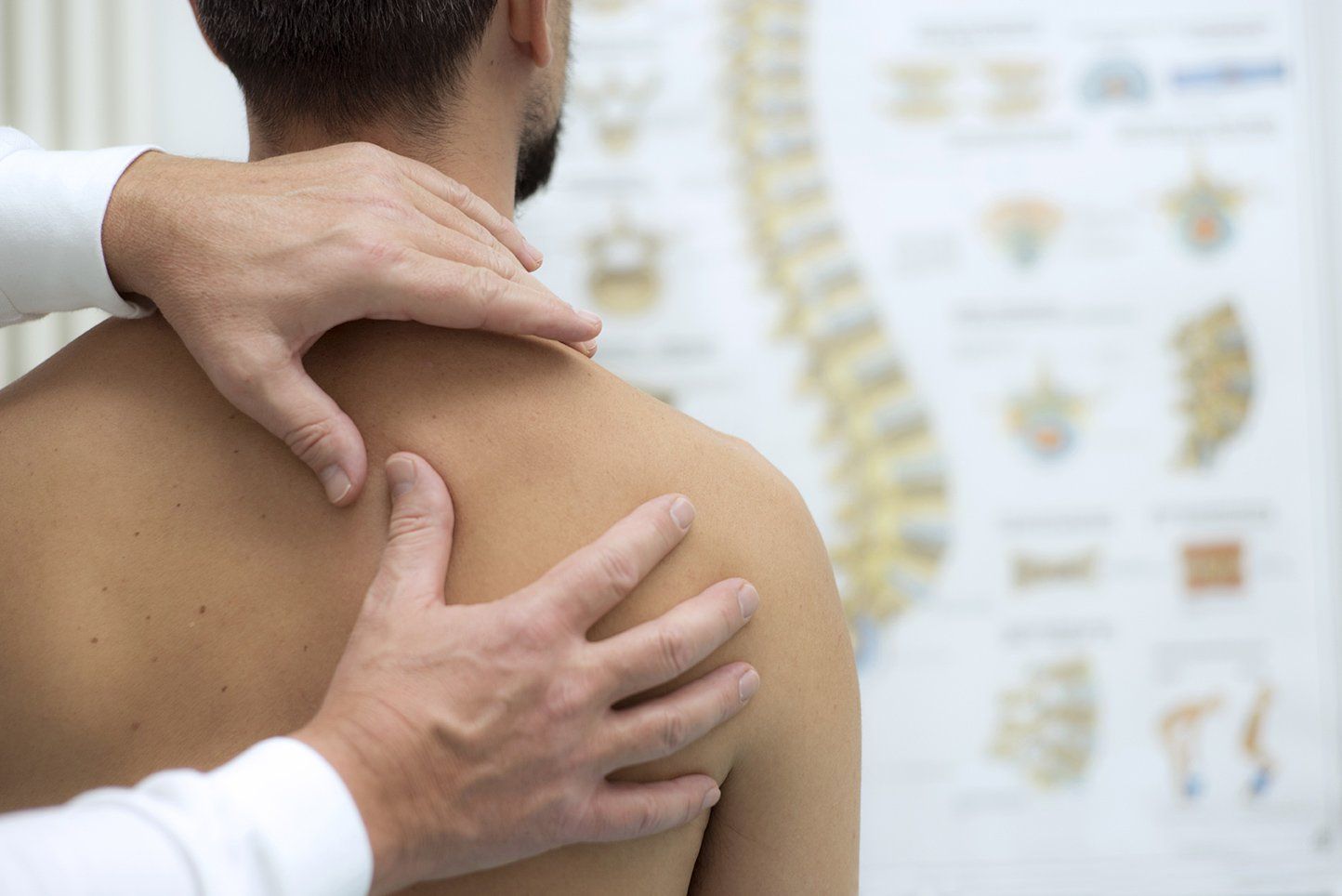
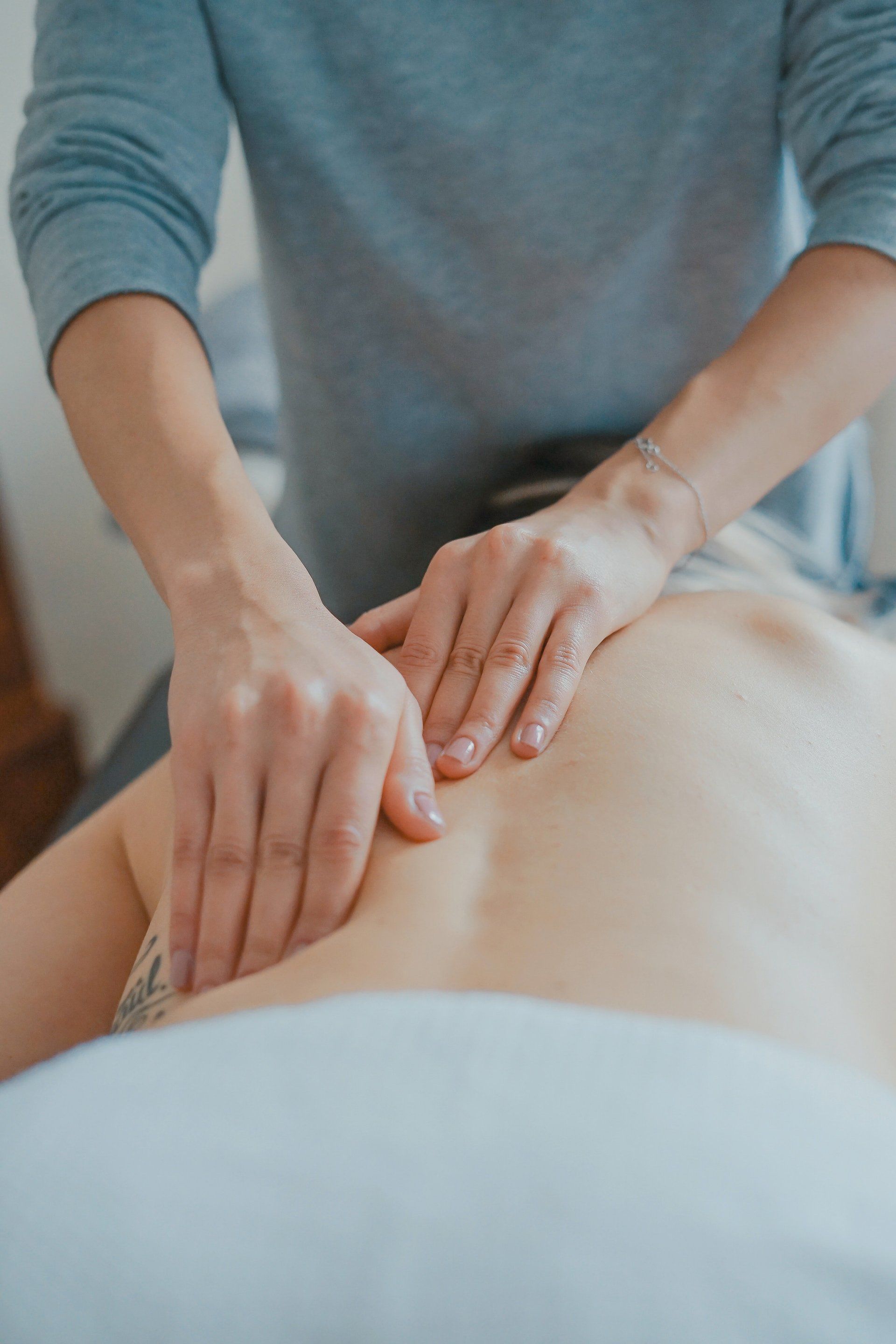
Family Chiropractic Plus
Offering Excellent Chiropractic Healthcare In St. Petersburg, Florida.
BOOK AN APPOINTMENT
WELCOME TO
Family Chiropractic Plus
Family Chiropractic Plus is working diligently to be the very best St Petersburg Chiropractors so we are YOUR CHOICE for St. Petersburg chiropractic care!
Dedicated to your good health
Family Chiropractic Plus is dedicated to your overall health and well-being. Which is why we offer manual chiropractic adjustments in order to restore your body’s natural state of optimal health, while also providing it with the support it needs to heal from any injury, big or small.
Want to learn more? Fill out the form to get started!
Contact Us
How We Can Help
Take a look at our services and choose the one that best fits your needs.
Manual Adjustment
Are you struggling with pain in your lower back or neck? Chronic headaches and tingling? Then our manual adjustment is for you.
Nutritional Counseling
Family Chiropractic Plus fully understands the connection between diet and wellness. We are here to help you with all your nutritional needs.
Massage Therapy
Massage therapy benefits our patients in many ways, so we proudly offer this service as part of our chiropractic care options!
Physical Therapy
Physiotherapy is an important part of any rehabilitation program. This is why at Family Chiropractic Plus, we offer a comprehensive physiotherapy program.
Ready To Relieve Symptoms and Reach a Higher Level of Body Performance?
Request an appointment today!
Where It All Begins
At Family Chiropractic Plus in St. Petersburg, we are committed to nothing less than the best for our valued patients, which begins with a phenomenal staff!
Our goal is that you don’t simply get rid of back pain temporarily, but that you are able to achieve a higher level of health, well-being and overall happiness. To facilitate this goal, we employ all the tools in our repertoire, including full-body chiropractic adjustments, nutritional counseling, and multiple physical therapy strategies.
Satisfied Patients
"Dr Martin has been the best Chiropractor I have found in Florida, he is not only skilled, but compassionate, caring and in tune with all your needs."
Sandi M
The family-run practice for Family Chiropractic Plus is truly a stand-alone excellent practice. They don't just say they put their patient care first, they actually do. They have amazing integrity and are welcoming and friendly. I highly recommend Family Chiropractic Plus for your health needs!
Dr. Cori
"Very pleased with how the doctor went above and beyond the norm to determine what was going with my body and how he explained to me what was needed to get better."
Louise Baines
Ready To Relieve Symptoms and Reach a Higher Level of Body Performance?
Request an appointment today!
OUR BLOG
We hear it all the time at Family Chiropractic Plus: "I don't need an adjustment; I just cracked my own back this morning!" It’s a tempting habit. When you feel stiff or sore, you might twist, bend, or push on your spine until you hear that familiar "pop," followed by a fleeting moment of relief. But while that release might feel good for a few minutes, self-adjusting is a far cry from professional chiropractic care—and in many cases, it’s actually making your condition worse. Here is why you should stop "self-cracking" and start seeking specific care. 1. It Lacks Specificity When you force your spine to pop, you aren't targeting the actual joint causing the trouble. Instead, you are moving multiple joints at once—usually the ones that were already moving just fine. Chiropractic adjustments are an art of precision. We use diagnostic tools, including digital X-rays , to identify the exact joint that is misaligned or restricted. We then apply a specific force to that area only. Without that level of precision, you’re just making "noise" without correcting the underlying issue. 2. You Are Creating Hypermobility (Instability) This is the most common danger of self-adjusting. When you force your joints to pop, you are often overstretching the ligaments around joints that are already mobile. Over time, these joints become hypermobile (too loose), while the "stuck" joints remain restricted. This imbalance puts massive stress on your spinal cord, muscles, and ligaments. Eventually, this instability can lead to chronic pain and even premature joint degeneration. 3. You Aren't Fixing the "Stuck" Joint The reason you feel the urge to crack your back again an hour later is because the problem joint — the one that is truly restricted — never actually moved. You’ve only manipulated the segments above and below it. It becomes a vicious cycle: you pop the wrong joints, feel a temporary endorphin rush but the original restriction remains. A professional chiropractor breaks that cycle by unlocking the specific joint that needs it. Once the true restriction is corrected that constant "urge" to crack usually disappears. 4. The Risk of Injury Your spine houses your central nervous system — it is delicate. Forcing your neck or back in the wrong direction can result in strained tendons, irritated nerves or even a rib displacement. Professional adjustments are controlled, safe and backed by years of clinical training. Leave It to the Pros in St. Pete Chiropractic care isn't about making noise; it’s about restoring function and allowing your body to heal. At Family Chiropractic Plus , we don't guess—we test. By using hands-on analysis and X-rays, we find the specific areas that need attention and adjust them safely. The next time you feel the urge to "crack" your own back, remember: the risks far outweigh the short-lived relief. Give your spine the professional care it deserves. Ready for a real adjustment? Contact Family Chiropractic Plus in St. Petersburg today to schedule your evaluation!

Do you ever feel like you’re walking through a mental haze? Maybe you find yourself staring at your computer screen at work, re-reading the same sentence or forgetting why you walked into a room. At Family Chiropractic Plus, we meet many St. Petersburg residents who struggle with "brain fog"—that frustrating combination of slow thinking, forgetfulness and a lack of concentration. While most people blame poor sleep or caffeine crashes, there is a physical source for mental clarity that many overlook: your spinal alignment. The Brain-Body Highway At our St. Petersburg clinic, we often describe the spine as more than just a support structure—it is the main highway for communication between your brain and every other part of your body. When your spine is properly aligned, nerve signals travel at lightning speed, which allows for sharp cognitive function. However, when misalignments (known as subluxations) occur, they act like traffic jams on the Howard Frankland Bridge—delaying essential messages and causing "static" in your nervous system. This interference doesn't just cause back pain; it can significantly dull your mental edge. What is Brain Fog, Really? While not a formal medical diagnosis, brain fog is a sign that your body is under stress. It can be triggered by: • Chronic inflammation • Spinal tension and "Tech Neck" • An overactive "fight or flight" response When your nervous system is out of balance, your brain is forced to spend extra energy just to maintain basic functions which leaves you feeling mentally exhausted before the day has even truly begun. How Chiropractic Adjustments Clear the Haze Our adjustments at Family Chiropractic Plus are designed to restore proper movement and alignment, effectively "clearing the tracks" for your nervous system. By removing pressure from the nerves, we help your brain send and receive signals with 100% efficiency. Many of our patients report a "lightbulb moment" following a series of adjustments, feeling more focused, emotionally lighter and mentally sharp. This isn't magic; it’s simply the result of your body operating exactly as it was designed to. Additional Brain-Boosting Benefits Beyond clearing the fog, regular care at our office can help: • Lower Stress & Anxiety: Calming the nervous system helps you stay "cool" during the St. Pete rush hour. • Improve Sleep Quality: Better alignment leads to deeper recovery cycles. • Boost Oxygen Flow: Better posture opens the chest and neck, ensuring your brain gets the oxygenated blood it needs to thrive. Unlock Your Best Version You weren't meant to just "survive" your day—you were meant to thrive. If you’re tired of feeling foggy and are ready to regain your focus, our team is here to help. Ready to clear the fog? Contact Family Chiropractic Plus in St. Petersburg today to schedule your evaluation and start your journey toward a clearer, more focused you!

Celebrating Deaf Awareness Month: A Commitment to Communication and Wellness September is Deaf Awareness Month, a time dedicated to celebrating the rich culture, language and contributions of the Deaf and Hard of Hearing community. Here at Family Chiropractic Plus, we see this as more than just an observance; it’s a powerful reminder that true health and wellness are built on a foundation of clear communication, understanding and inclusivity. Communication is the bridge that connects us. In healthcare, that bridge is essential. When communication is clear, accessible and respectful, patients feel seen, heard and empowered. For members of the Deaf community, navigating a world that primarily communicates through sound can present significant barriers, especially in a healthcare setting. We believe it is our responsibility to help break down those barriers. Our Commitment to the Deaf Community in St. Petersburg Our mission at Family Chiropractic Plus is to help you become the very best version of yourself, and that promise extends to every member of our community. We are committed to providing a welcoming, accessible and supportive environment for our Deaf and Hard of Hearing patients. We understand that effective communication is key to your care. Our team is dedicated to: • Ensuring We Understand You: We are prepared to utilize various communication methods, including writing, visual aids, and are happy to work with Video Remote Interpreting (VRI) services or a patient-provided ASL interpreter to ensure consultations are clear and comfortable. • Providing Patient-Centered Care: We take the time to listen, ensuring you are a full partner in your healthcare journey. Your comfort and understanding are our top priorities. • Creating a Safe Space: We are dedicated to fostering an environment of respect and patience, where every individual feels valued and understood. Wellness is for Every Body Just as your nervous system is the communication highway for your body, clear communication is the pathway to holistic wellness. Chiropractic care helps ensure your body's internal communication lines are functioning optimally. In the same spirit, we strive to ensure our communication with you is just as clear and effective. This Deaf Awareness Month, we celebrate the strength and vibrancy of the Deaf community. We also reaffirm our commitment to being a healthcare partner you can trust. Your journey to health starts with being understood. Contact our St. Petersburg clinic today to learn more or to schedule your appointment.